Table of Contents
V6Z80P Hardware description
Hardware overview

V6Z80P Brief circuit description
The entire V6Z80P system runs from a 16MHz (3.3v) TTL clock source. This feeds the FPGA, the Z80 (via a 74HCT08 AND gate acting as a voltage shifter because of the V_level requirements of its clock input) and the config PIC.
Memory buses
- “Video memory” - 512KB 10ns, direct connection. Chip always selected.
- “Sprite memory” - 128KB 10ns, direct connection. Chip always selected.
- “System memory” - 512KB 25ns, direct connection with D0-D7, A0:A14, /RD and /WR routed to the relevent Z80 pins. System RAM A18:A15 are conneced only to the FPGA, Z80 A15 also has its own seperate FPGA connection - this allows the Z80 address space to be paged in two halves. System RAM chip select is also connected to the FPGA.
CPU connections
All Z80 control pins (except from RFSH and HALT which arent used) are connected to FPGA pins.
Peripherals
Audio
Two outputs from the FPGA (Sigma/Delta pulse trains) drive a simple resistor/capacitor filter. The output of which has its amplitude halved by a potential divider (2 x 10K), passed via 1uf capacitor to the left and right of the audio socket.
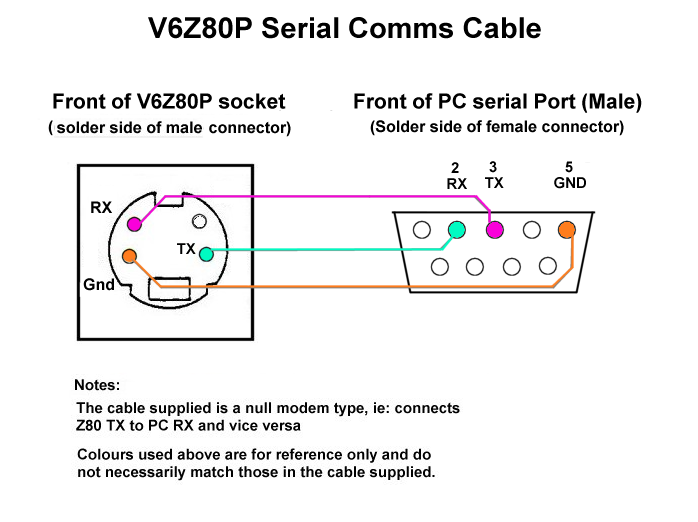
Serial Port
To connect to a standard RS232 serial port - RX and TX only are implemented. The lines are routed via a ST232 level converter chip to and from the FPGA.
Serial comms schematics:
Video Port
12 FPGA ouputs drive 3 x 4 resitor DACs, this allows a palette of 4096 colours. The RGB levels are <0.7v suitable for TV for VGA monitor. 2 additional FPGA outputs drive Horizontal and Vertical sync. The vertical sync is available as direct TTL level (for VGA) and via a 750 Ohm resistor for TV levels. Horizontal sync is only used for VGA and is therefore TTL. A “select” output (5volts via a 100 Ohm resistor) is available to engage RGB mode on TVs - this is hardwired and does not use an FPGA pin)
Audio and video schematics:

PS2 ports
Keyboard and mouse. CLOCK and DATA directly connected to FPGA. These lines can also be pulled down (for output) on the VxZ80P side by transistors connected to the FPGA. (8 FPGA pins used in total).
Keyboard and mouse schematics:

Joysticks
Two ATARI 2600 style connectors: 6 inputs each. (Megadrive pads can also be sed following a minor hardware modification). Lines are pulled up by resistors on the PCB and pulled low by the switches in the joystick. The 12 lines are connected to a PIC 16F62x microcontroller which acts as a parallel-to-serial converter. Two FPGA pins for Clock and Data are used to read the joystick data.
Joystick:

MMC/SD memory card
Uses 5 FPGA pins to connect to Power, /Card Select, Data_in, Data_out and Clock. /Card select is also connected to an LED via resistor for access indication. The FPGA /Power line switches a PNP transistor to apply power to the card.
SD card interface schematics:

Other pins connected to the FPGA
There are 6 pins available to use for external connections via a pin header near the video socket. (In the default V6Z80P FPGA architecture, 3 of these pins are used for video type select, reset and NMI inputs, the other 3 are free I/O ports.)

The configuration system uses several FPGA pins to upload config and communicate with the PIC controller dedicated to this task (includes reprogramming the EEPROM etc)

JTAG port
Used for “live” config of the FPGA, standard Xilinx pin out sequence.
Config selection jumper
Selects between JTAG mode and normal EEPROM config (slave serial mode)
